Use smartphone as a webcam
Droidcam makes the setup easy on Linux
These days of coronavirus where a lot of people work from home the number of teleconferences per unit of time has skyrocketed. Most of us are forced to use video conferencing software of dubious privacy practices1 without having much say in the choice, but that is a story for another day. If you are like me and do not have an external webcam to plug into your PC, don’t run off to the store just yet. There are solutions to make your Android smartphone act as a webcam that work really well. One of them is droidcam from Dev47Apps, which works even if you don’t have Google Services installed. This post quickly discusses how to set this up on your Linux PC using both wifi and ADB.
Installing droidcam
First, install the droidcam app in your phone, and download and unpack the Linux version wherever. Then, follow the instructions here to install it. You will have to launch the app on your phone before attempting the connection from your PC.
Using droidcam via WiFi
This is the easiest way to connect the phone camera to your PC. For this to work, the phone and the computer must be on the same local network. The phone will be connected via wifi, and the computer may either be wired or wirelessly connected.
Open the app on your phone and take note of the wifi IP and port. Then, cd to the droidcam installation folder and do:
droidcam-cli <ip> <port>
If the connection succeeds, you will see that the camera on your phone is active, and the image shows up on the phone screen. You can test it by feeding the video device stream to mpv:
mpv av://v4l2:/dev/video0
Replace the /dev/video0 with your device file.
Using ADB over USB
Sometimes, you can’t connect the phone and the computer to the same local network. For instance, at my work, the computer is wired to the institute network, but the only wifi available is eduroam. In cases like this, you can still get a connection over the Android Debug Bridge (ADB) via USB. You will need a USB cable to connect your phone to your computer. Also, you need to activate the developer options on your phone and enable ADB debugging.
Once that is done, install adb on your Linux box. Most distros will just have it in their repositories. On Arch, do:
pacman -S android-tools
On Debian and derivatives, you would run:
apt install adb
Once adb is installed, check that the device is connected correctly. You may need to confirm the connection in a pop-up dialog on your phone.
$ adb devices
List of devices attached
631e718c device
Finally, launch droidcam on your device and attempt the connection from your Linux box,
droidcam-cli adb <port>
where <port> is the port listed on the droidcam interface in your phone. Again, check that video works with:
mpv av://v4l2:/dev/video0
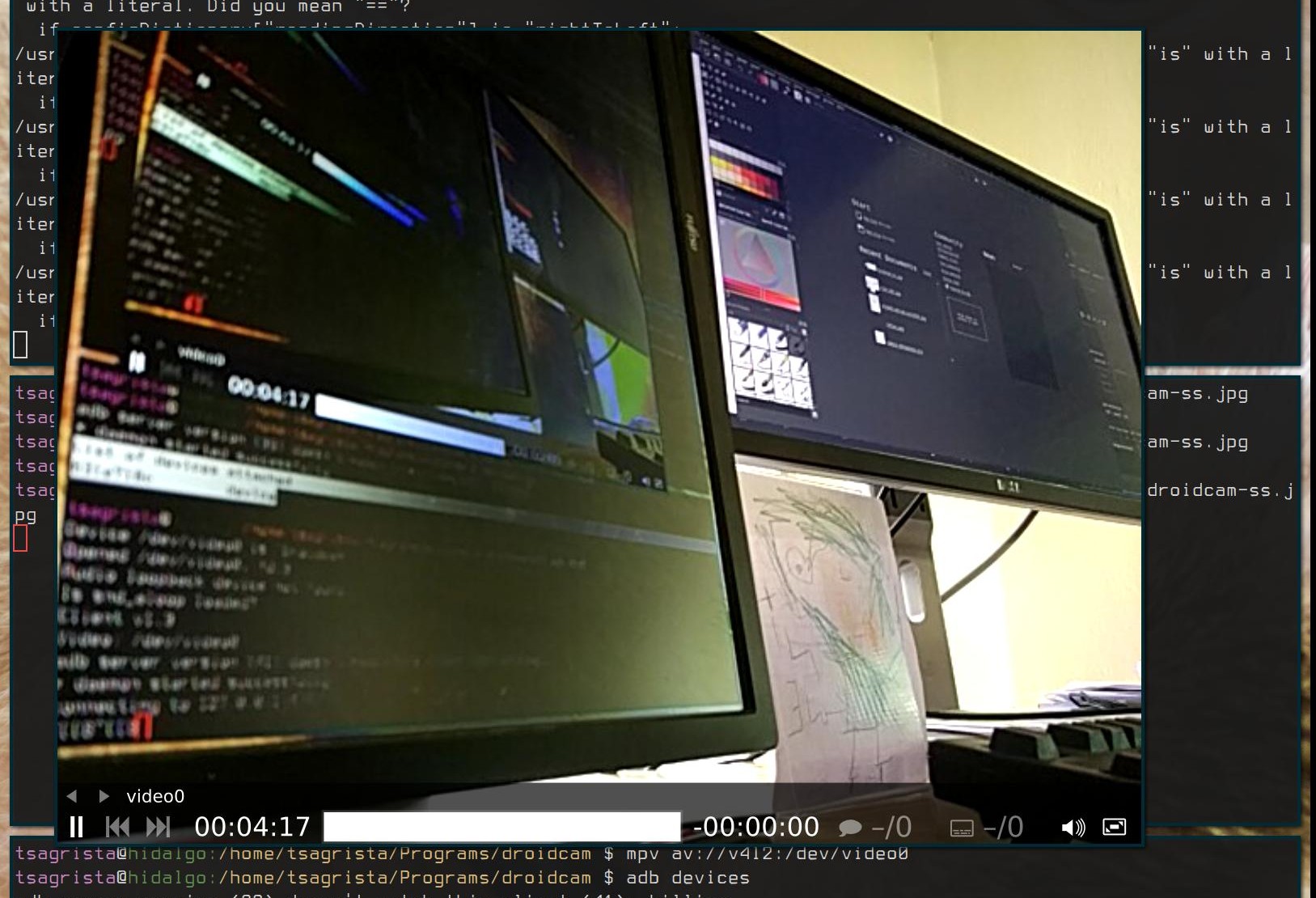
Smartphone camera feed playing on mpv.
Final notes
We have seen that it is quite easy to use a smartphone as a webcam on Linux. Right now, webcams are quite expensive due to the high demand, so this may be a good alternative for you, as it is for me. You can even use an old device and re-purpose it as a webcam, effectively extending its life, avoiding unnecessary expenses in new gadgets at the same time.